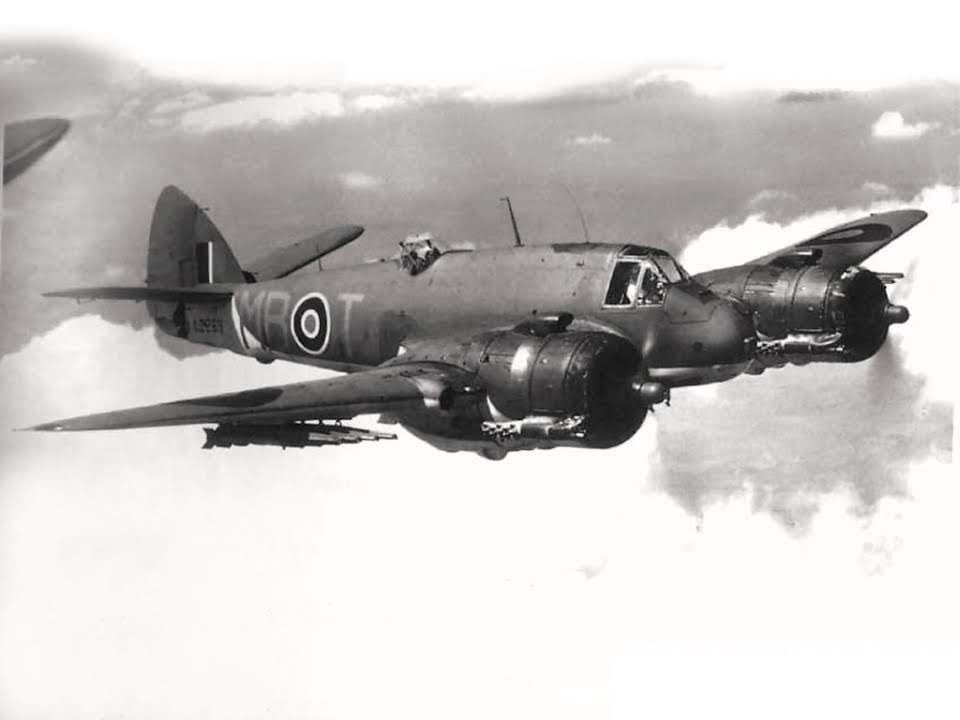
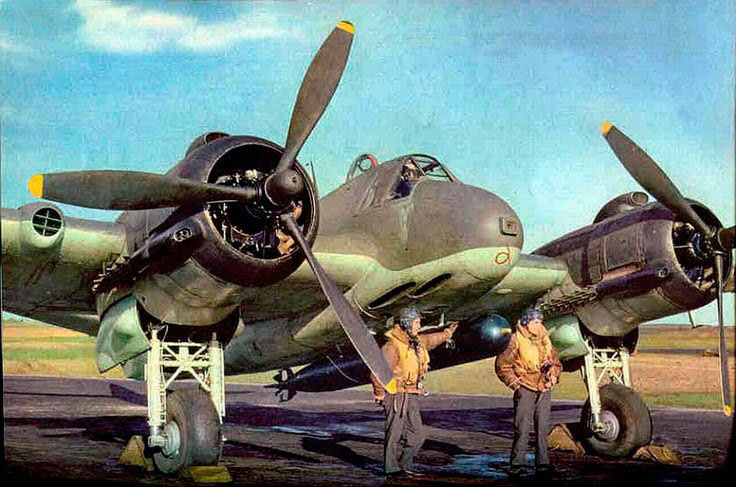
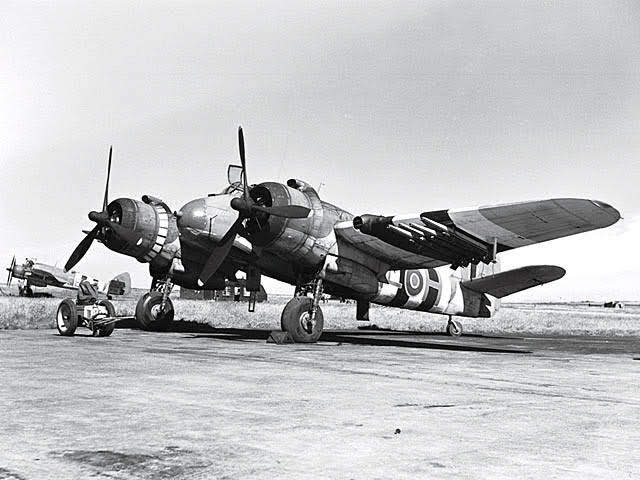
Bristol ‘Beaufighter’
At the start of Luftwaffe night bombing raids, the ‘Beau,’ initially conceived as a heavy fighter/bomber, was the only viable candidate as a defence against the bomber streams. After a slow start, the installation of the AI radar, and ground control coordination quickly improved it’s effectiveness, and she became highly efficient in the night fighter role, heavily armed with 4 x 20mm mk2 Hispano cannon mounted in the nose, her firepower proved devastating against enemy bombers, As its wartime service continued, the Beaufighter was used in many different roles; receiving the nicknames Rockbeau for its use as a rocket-armed ground attack aircraft, and Torbeau in its role as a torpedo bomber against Axis shipping, in which it came to replace the Beaufort which had preceded it. In later operations, it served mainly as a maritime strike/ground attack aircraft, RAF Coastal Command having operated the largest number of Beaufighters amongst all other commands at one point. The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) also made extensive use of the type in the maritime anti-shipping role, such as during the Battle of the Bismarck Sea.
The Beaufighter saw extensive service during the war with the RAF (59 squadrons), Fleet Air Arm (15 squadrons), RAAF (seven squadrons), Royal Canadian Air Force (four squadrons), United States Army Air Forces (four squadrons), Royal New Zealand Air Force (two squadrons), South African Air Force (two squadrons) and Polskie Siły Powietrzne (Free Polish Air Force; one squadron). In addition, variants of the Beaufighter were also manufactured in Australia by the Department of Aircraft Production (DAP); such aircraft are sometimes referred to by the name DAP Beaufighter.




Recent Comments